For Appointments,
044 4524 2407What is Hernia
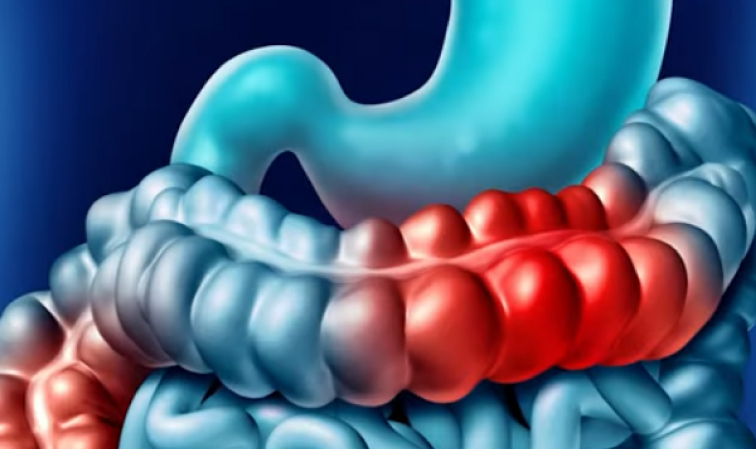
- A hernia is a condition in which an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak point or tear in the muscle or surrounding tissue that holds it in place.
- There are several types of hernias, including inguinal (inner groin), Umbilical (intestine bulge through the abdominal wall), and Ventral (tissue bulges through an opening in the muscle of your abdomen) etc.,
- Hernias can cause pain and discomfort, if left untreated, and it can lead to serious complications. It is important for individuals to be aware of the signs and symptoms of hernias, as well as the risk factors and preventative measures. Early detection and treatment can prevent the hernia from becoming larger and more difficult to repair.
Key Benefits of Rebuild Hernia Treatment

Pain Relief
Alleviates discomfort and pain associated with the hernia.
Prevents Complications
Reduces the risk of serious issues like bowel obstruction or strangulation.

Restores Functionality
Improves the ability to perform daily activities without pain or restriction

Improves Quality of Life
Enhances overall well-being and comfort.
Strengthens Abdominal Wall
Reinforces the weakened area to prevent recurrence.
Faster Recovery
Modern surgical techniques can lead to quicker and more effective recovery.
Types of Hernia
Femoral Hernia
It occurs when the intestine protrudes through the femoral canal, which is located in the upper thigh.
Inguinal Hernia
It is the most common type of hernia and occurs when the intestine or bladder protrudes through the inguinal canal, which is located in the groin area.
Incisional Hernia
It occurs at the site of a previous surgery, where the scar tissue is weak, and the intestine protrudes through the muscle.
Umbilical Hernia
It occurs when a part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal muscles near the navel.
Hiatal Hernia
It occurs when the upper part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity.
Testimonials
Our Doctors

Senior Consultant and Clinical Lead
Dr. Deepak Subramanian
General, Minimal Access (GI) & Bariatric Surgery

Consultant
Dr Anirudh V
Department of Minimal Access (GI) and Bariatric Surgery
Causes Of Hernia
Symptoms of Hernia

Noticeable bulge or lump in the abdomen or groin area

Pain or discomfort, especially when bending over, coughing, or lifting

Constipation or changes in bowel habits (if the intestine is involved)

Burning, aching, or gurgling sensation at the site of the bulge

Difficulty swallowing (in the case of hiatal hernias)

Chest pain (in the case of hiatal hernias)
Weakness or pressure in the abdomen
Treatment Options for Hernias
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Watchful Waiting: For small, asymptomatic hernias, doctors may recommend monitoring the hernia to ensure it doesn't worsen.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary adjustments, avoiding heavy lifting, and managing body weight can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the hernia from getting worse.
- Hernia Truss or Belt: A supportive undergarment can help hold the hernia in place and relieve discomfort, though it does not treat the underlying problem.
Surgical Treatments
- Herniorrhaphy: Traditional open surgery where the hernia is pushed back into place and the weakened muscle wall is repaired.
- Hernioplasty: Similar to herniorrhaphy, but involves the use of a synthetic mesh to strengthen the muscle wall.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions, a camera, and special instruments to repair the hernia with or without mesh.
Comparison: Laparoscopic vs Open Repair
Aspect | Laparoscopic Repair | Open Repair |
Incisions | Small incisions (usually 3-5), less scarring | Larger single incision, more visible scarring |
Recovery Time | Shorter recovery time, quicker return to normal activities | Longer recovery time, more postoperative discomfort |
Hospital Stay | Often same-day discharge or one-day stay | May require a longer hospital stay |
Risk of Recurrence | Similar or lower risk when performed by experienced surgeons | Slightly higher risk, depending on hernia type and patient condition |
Complexity | Requires specialized skills and equipment | More straightforward, generally available |
Pain Relief | Significant pain relief | Significant pain relief |
Durability | Long-term solution with low risk of recurrence | Long-term solution, risk varies with technique and patient condition |
Suitability | Suitable for patients withmultiple or bilateral hernias, and those seeking quicker recovery | Suitable for patients with larger, more complex hernias, or those who cannot undergo laparoscopic surgery |