Appointment
Please Select the type of appointment you would like to book
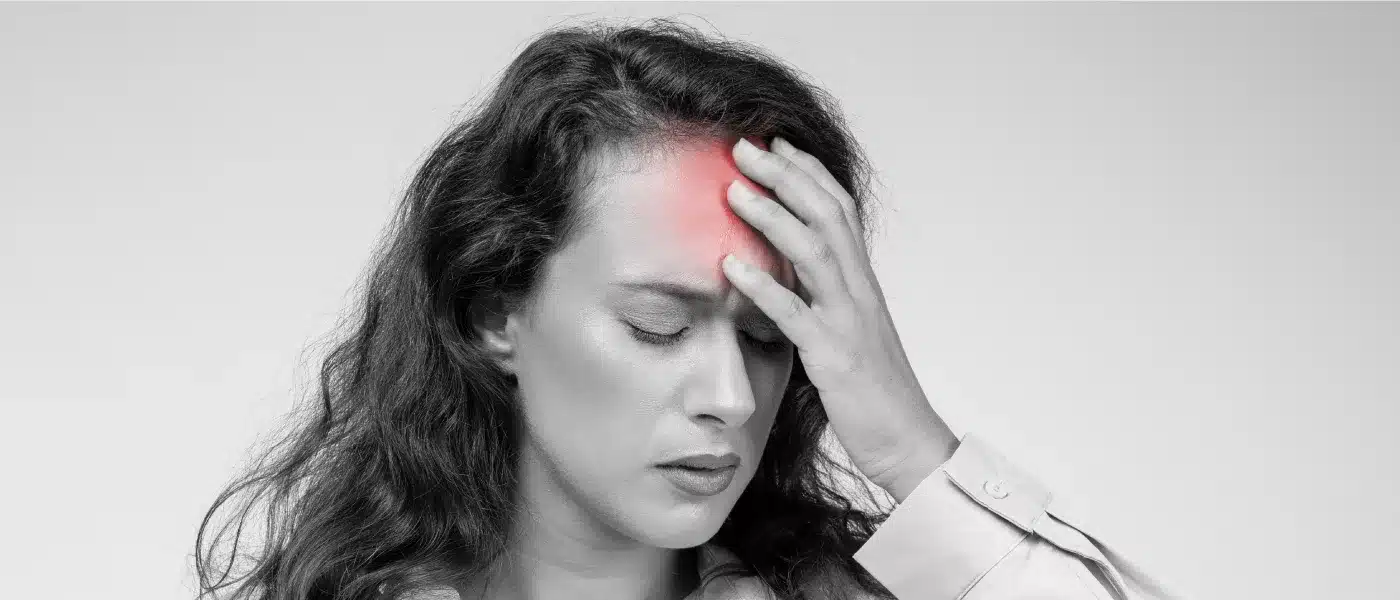
The silent pulsating noise in your head Thu , Mar 14

About the Health Information
Our Health information will help you stay up to date on what is happening in health care. We bring you news/information/perspectives around health care innovations, preventive medicine, early diagnosis, nutrition and diet, women’s health, men’s health, children’s health, latest technologies, treatments and surgeries, diseases and conditions, fitness and more.
Popular Posts

Health Tips
Wed , Apr 8
Six daily shoulder exercises for arthritic pain

Medical Emergency
Mon , Dec 27
Shoulder Arthritis and its types

Health Tips
Wed , Apr 8
Stress and how to beat it
Categories
- Cancer
- Cardiac Care
- Children's Health
- Covid-19
- Diabetes
- ENT
- Health Emergencies
- Health Tips
- Hernia
- Hospitals
- Interventional Pulmonology
- Kidney Stone
- Medical Emergency
- Men's Health
- Neuro Care
- Oral Cancer
- Orthopaedics
- Spine Care
- Stroke
- Transplants
- Women's Health
- World Brain Day
- World Health Day
- World Hearing Day
- World Kidney Day
- World Sleep day
- World Vaccination Day
Migraine, a prevalent neurologic condition, causes strong headaches affecting millions daily. Recognising its widespread impact, the World Health Organisation has classified migraine as the third most disabling medical condition.

 In-person Consultation
In-person Consultation Online Video Consultation
Online Video Consultation Treatment Enquiries
Treatment Enquiries Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Access the Patient Portal
Access the Patient Portal +91 44 4524 2407
+91 44 4524 2407  Minimal Access GI & Bariatric Surgery
Minimal Access GI & Bariatric Surgery Multi-Visceral and Abdominal Organ Transplant
Multi-Visceral and Abdominal Organ Transplant Neurology
Neurology Spine Surgery
Spine Surgery Total Knee replacement
Total Knee replacement Anaesthesiology & SICU
Anaesthesiology & SICU Paediatric Cardiology
Paediatric Cardiology Emergency Na MGM
Emergency Na MGM IVF
IVF Oncology Treatments
Oncology Treatments