Appointment
Please Select the type of appointment you would like to book
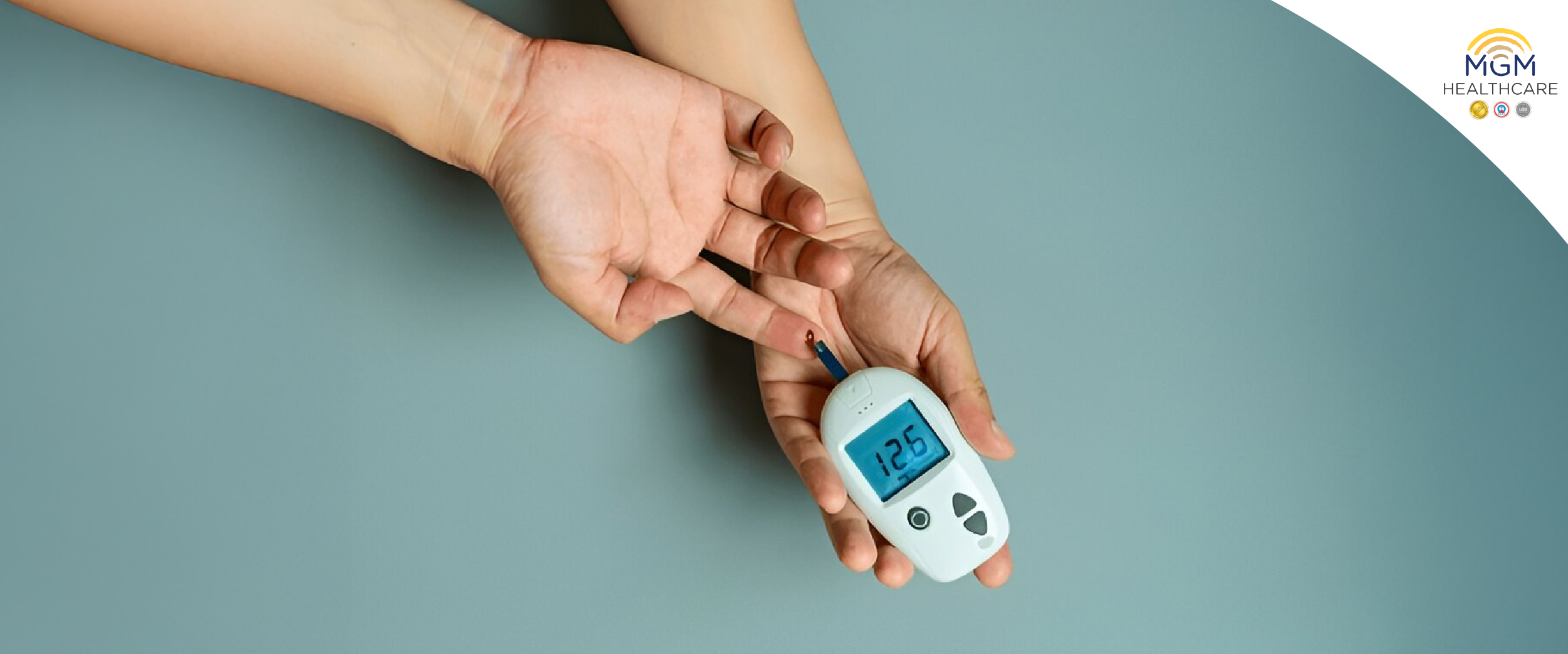
Diabetes Mellitus: Symptoms, Types, Diet, and Early Awareness Mon , Dec 1
About the Health Information
Our Health information will help you stay up to date on what is happening in health care. We bring you news/information/perspectives around health care innovations, preventive medicine, early diagnosis, nutrition and diet, women’s health, men’s health, children’s health, latest technologies, treatments and surgeries, diseases and conditions, fitness and more.
Popular Posts

Six daily shoulder exercises for arthritic pain

Shoulder Arthritis and its types

Stress and how to beat it
Categories
- Cancer
- Cardiac Care
- Children's Health
- Covid-19
- Diabetes
- ENT
- Health Emergencies
- Health Tips
- Hernia
- Hospitals
- Interventional Pulmonology
- Kidney Stone
- Medical Emergency
- Men's Health
- Neuro Care
- Oral Cancer
- Orthopaedics
- Spine Care
- Stroke
- Transplants
- Women's Health
- World Brain Day
- World Health Day
- World Hearing Day
- World Kidney Day
- World Sleep day
- World Vaccination Day
-
Diabetes affects more than just blood sugar. It impacts energy, immunity, mental health, and long-term wellbeing. With modern lifestyles and rising stress, early awareness of diabetes is more important than ever.
Recognising diabetes symptoms early helps prevent complications and supports better long-term health.
Why Early Awareness of Diabetes Matters
-
Diabetes develops slowly, and early signs are often ignored or mistaken for fatigue or stress.
Early awareness helps to:
- Reduce heart, kidney, and nerve complications
- Improve physical and mental wellbeing
- Identify diabetes risk factors early
- Enable timely testing and treatment
What Is Diabetes Mellitus?
-
Diabetes mellitus is a condition where the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot use it properly. This causes high blood sugar levels that may damage organs over time.
The two main types are:
- Type 1 diabetes – little or no insulin production
- Type 2 diabetes – insulin resistance, often lifestyle-related
What Is Diabetes Insipidus?
-
Diabetes insipidus is a rare condition affecting fluid balance, not blood sugar. Despite the name, it is not related to diabetes mellitus and requires different treatment.
Why Diabetes Is Increasing Today
-
Several lifestyle and health factors increase diabetes risk:
- Family history
- Overweight or obesity
- Processed and sugary foods
- Physical inactivity
- Chronic stress and poor sleep
- PCOS and gestational diabetes
Common Diabetes Symptoms
-
Watch for these common diabetes symptoms:
- Frequent thirst and urination
- Persistent tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Sudden weight changes
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
If symptoms persist, blood sugar testing is recommended.
Diabetes Diet and Food Choices
-
A balanced diabetes diet supports sugar control and overall health.
Diabetes food chart basics include:
- Whole grains and vegetables
- Lean proteins
- High-fibre foods
- Limited refined sugar
- Regular meal timings
Strengthening Diabetes Care
-
Diabetes management improves with:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring
- Healthy eating and daily activity
- Stress management
- Adherence to medical advice
- Diabetes education programs
Building Diabetes Awareness
-
Community awareness encourages early testing and healthy habits.
Simple steps include:
- Routine screening
- Health education programs
- Promoting exercise and balanced diets
- Supporting mental wellbeing
Conclusion
-
Early awareness, symptom recognition, and healthy lifestyle choices play a key role in managing diabetes. Informed decisions today can protect long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is caused when the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly. Common causes include genetics, unhealthy lifestyle habits, obesity, physical inactivity, and certain medical conditions.
Can diabetes be prevented?
Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through healthy eating, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress. Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented.
What foods should diabetics avoid?
People with diabetes should limit sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, fried foods, processed snacks, and sugary beverages, as these can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. It is commonly linked to lifestyle factors and genetics.
What is diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition where blood sugar levels remain high due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin use, potentially leading to long-term health complications.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, and unexplained weight changes.
How do you know if you have diabetes?
Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests such as fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, or oral glucose tolerance tests, especially if symptoms or risk factors are present.

 In-person Consultation
In-person Consultation Online Video Consultation
Online Video Consultation Treatment Enquiries
Treatment Enquiries Find a Doctor
Find a Doctor Access the Patient Portal
Access the Patient Portal +91 44 4524 2407
+91 44 4524 2407  Minimal Access GI & Bariatric Surgery
Minimal Access GI & Bariatric Surgery Multi-Visceral and Abdominal Organ Transplant
Multi-Visceral and Abdominal Organ Transplant Neurology
Neurology Spine Surgery
Spine Surgery Total Knee replacement
Total Knee replacement Anaesthesiology & SICU
Anaesthesiology & SICU Paediatric Cardiology
Paediatric Cardiology Emergency Na MGM
Emergency Na MGM IVF
IVF Oncology Treatments
Oncology Treatments